Building Solution
Energy-efficient cooling systems for buildings, designed to maintain optimal indoor air quality and comfortable.
Building Solution
Energy-efficient cooling systems for buildings, designed to maintain optimal indoor air quality and comfortable.
Cooling Innovation for the Future
Our energy-efficient cooling systems maintain building temperatures while reducing energy use, offering sustainable and cost-effective solutions for businesses and property owners.
With advanced technology, these systems optimize energy during peak and off-peak hours, integrating smoothly with building management systems. Our specialists ensure a seamless setup, allowing for immediate and long-term savings.
Cooling Innovation for the Future
Our energy-efficient cooling systems maintain building temperatures while reducing energy use, offering sustainable and cost-effective solutions for businesses and property owners.
With advanced technology, these systems optimize energy during peak and off-peak hours, integrating smoothly with building management systems. Our specialists ensure a seamless setup, allowing for immediate and long-term savings.
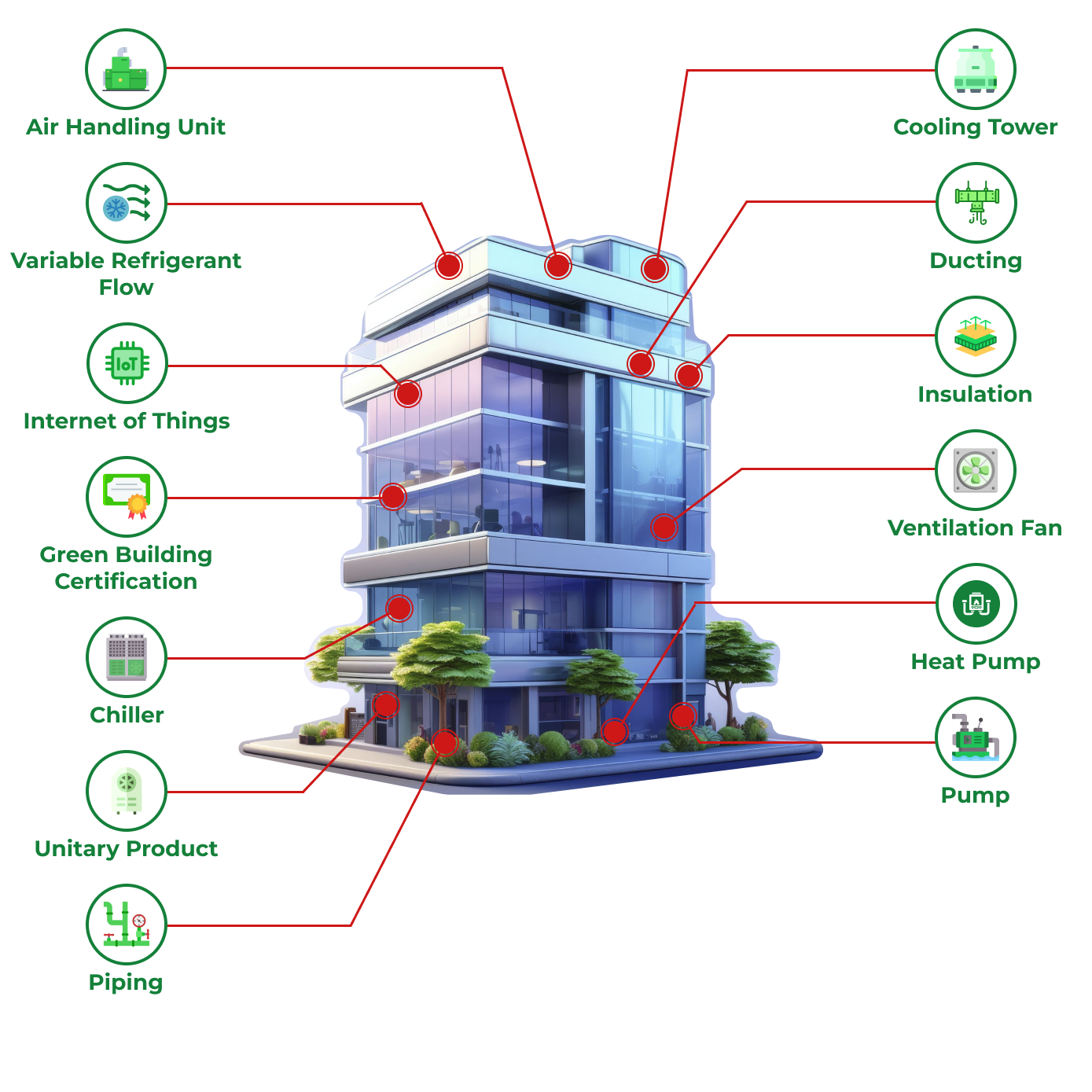
Chiller

is a type of cooling system that removes heat from a building or industrial process by transferring it to the surrounding air. It uses fans to blow air over the condenser coils, where the refrigerant releases heat and cools down. Unlike water-cooled chillers, air-cooled chillers do not require cooling towers or water, making them easier to install and maintain.
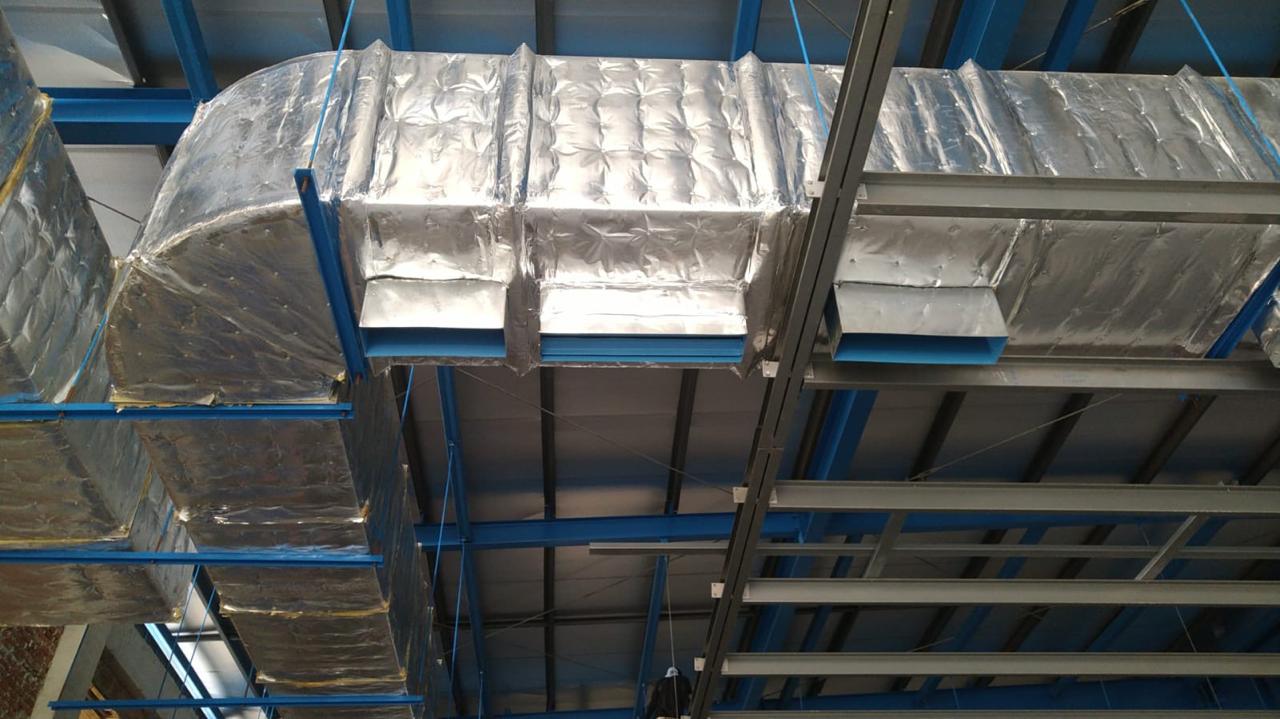
Ducting
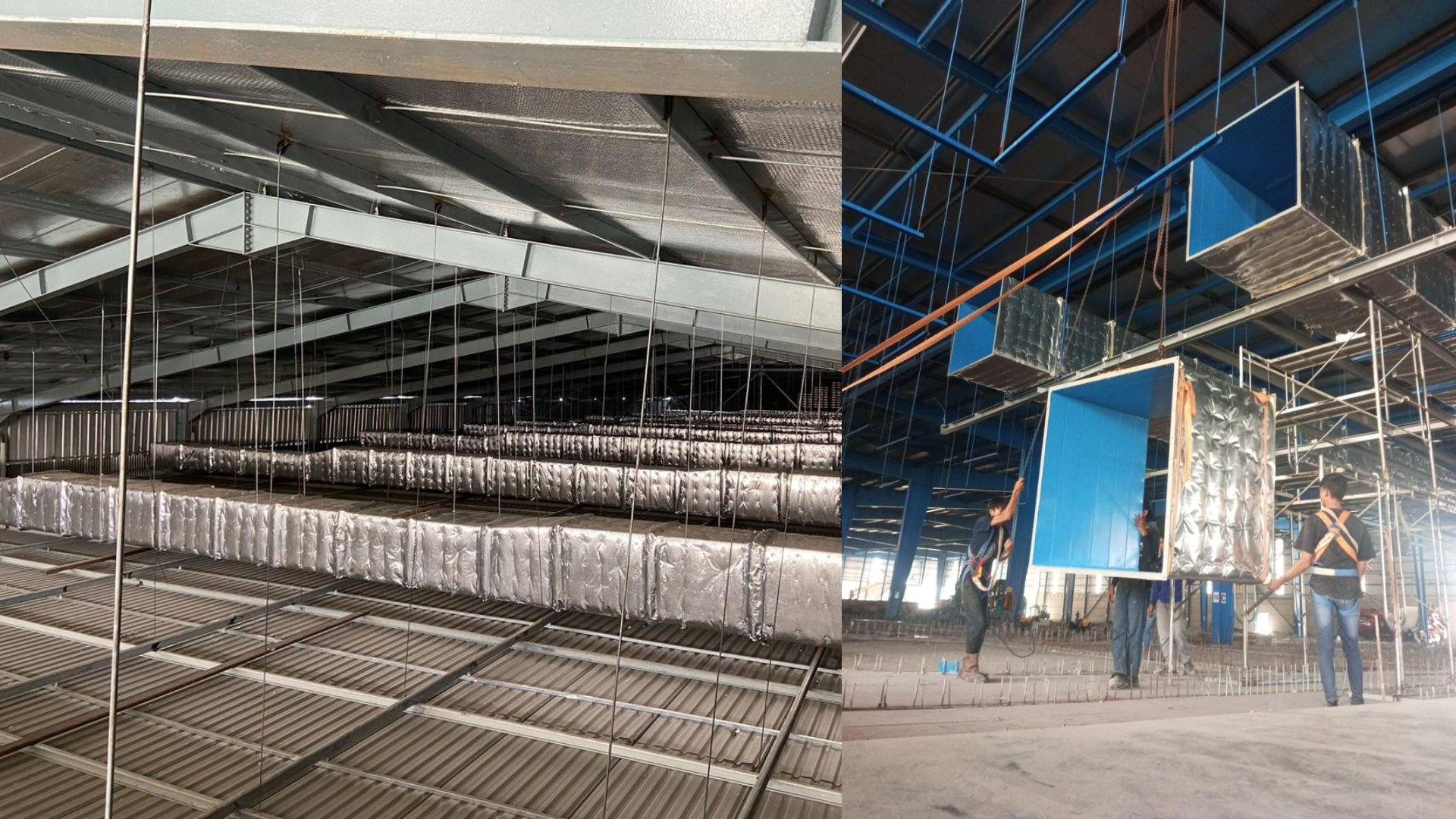

SGCI offers proper design and installation of ducting, essential for efficient airflow, energy conservation, and indoor air quality. In HVAC systems, ducting distributes heated or cooled air, including SUPPLY AIR DUCTS that deliver conditioned air to rooms and RETURN AIR DUCTS that return air to the unit for reconditioning.
EXHAUST AIR DUCT is used to exhaust air or gases from kitchens, bathrooms, laboratories, industrial processes, and other spaces where ventilation is necessary to remove pollutants, odors, or excess heat.
Chilled Water Piping
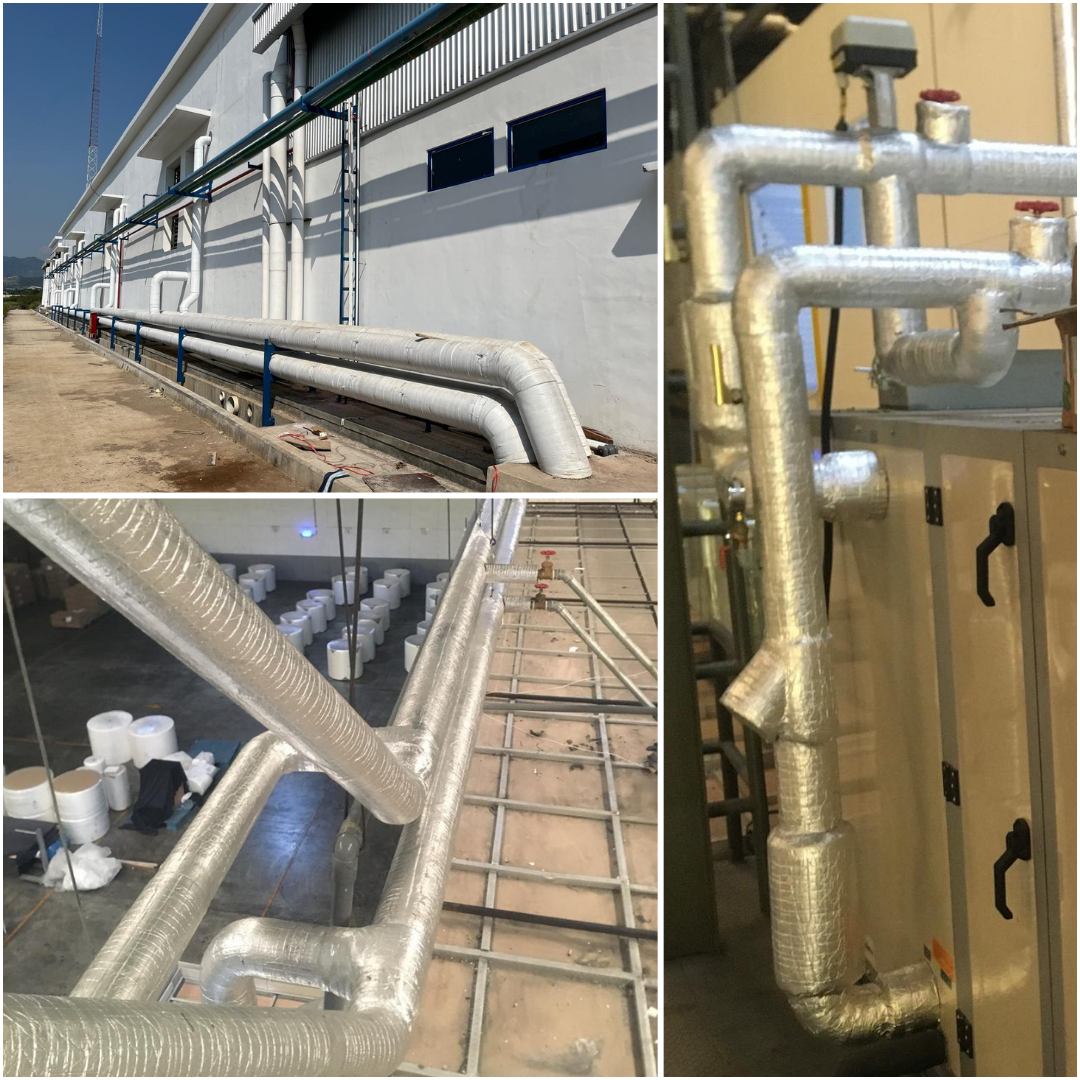

Chilled water piping and accessories are components used in a chilled water system to circulate cold water between the chiller and air handling units (AHUs) or fan coil units (FCUs) for cooling purposes. The chilled water absorbs heat from the building's air and is then pumped back to the chiller to be cooled again.
Pump
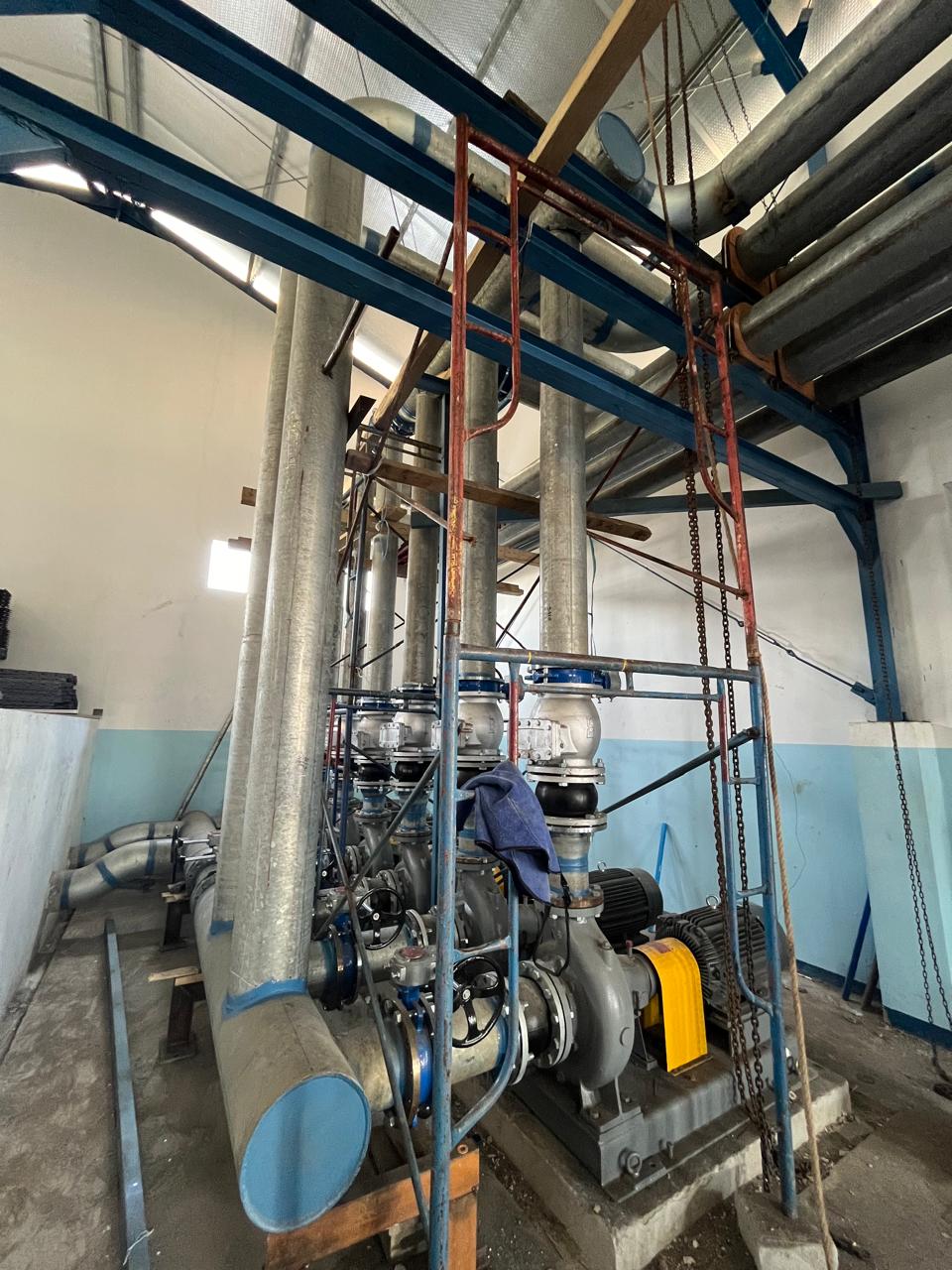

Pump systems efficiently move fluids across various applications, including industrial processes, HVAC systems, and water management. Utilizing mechanical energy, these systems ensure consistent flow and pressure while handling a wide range of liquids. Available in types like centrifugal and positive displacement, pumps can be tailored to meet specific operational needs, enhancing productivity and sustainability in diverse industries.
Cooling Tower
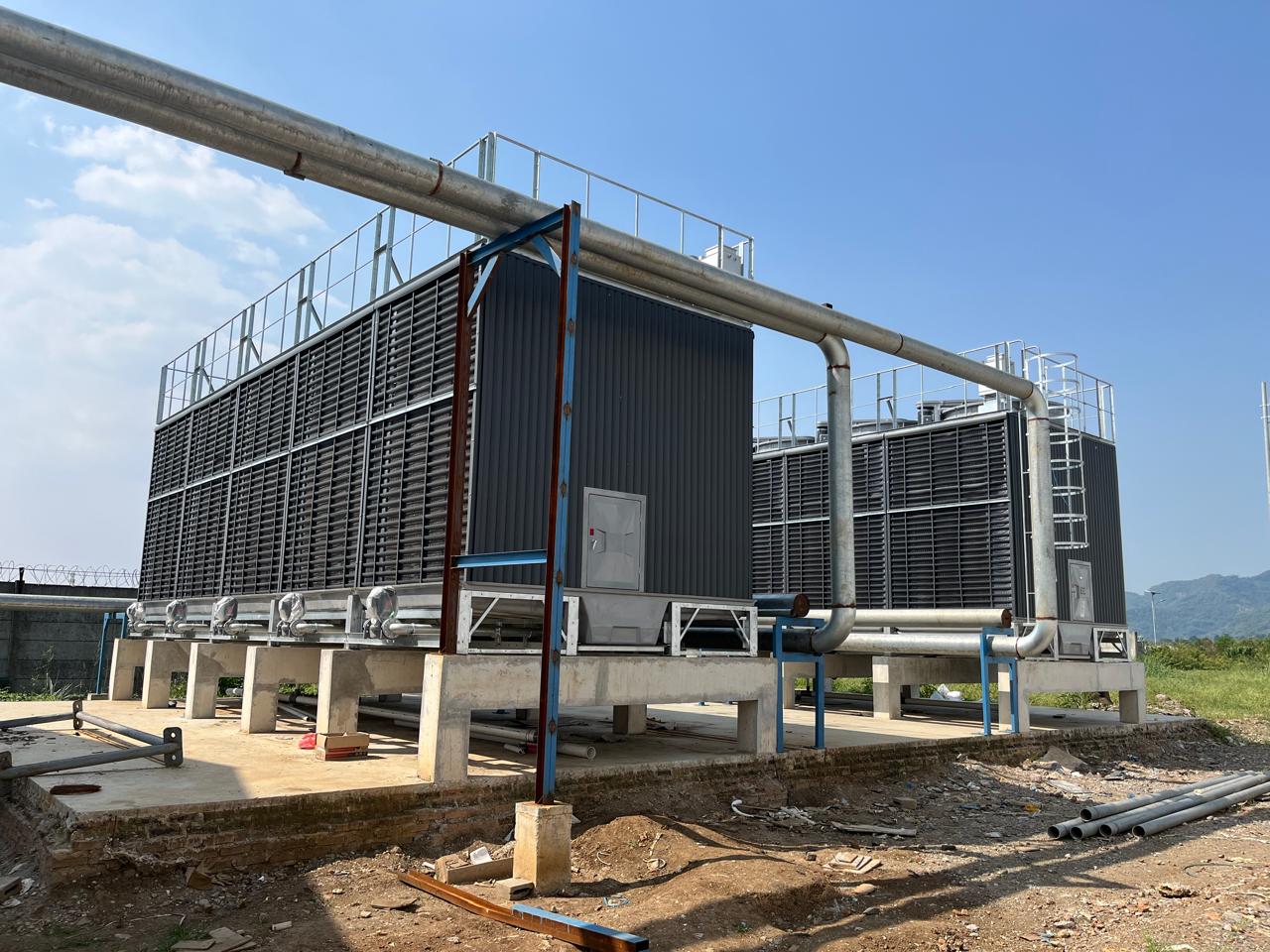

A cooling tower is a heat rejection device used to remove excess heat from a building or industrial process by cooling water. It works by transferring heat from the water to the outside air through evaporation.
Warm water from the system is pumped to the cooling tower, where it is sprayed over fill material to increase surface area. As air flows through the tower, some of the water evaporates, taking heat away with it and cooling the remaining water, which is then recirculated.
Air Handling Unit
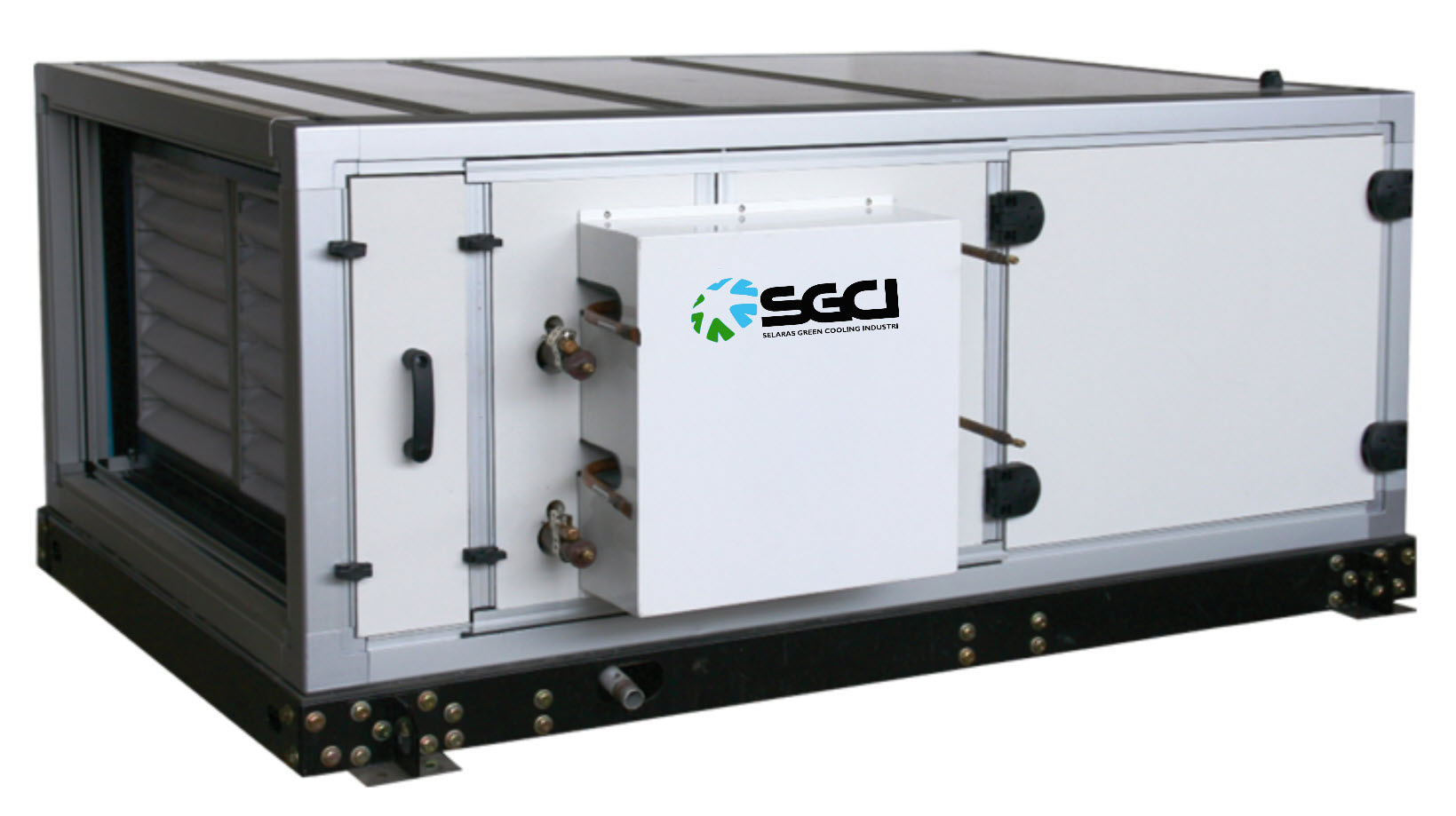

An AHU is a device in HVAC systems that regulates and circulates air for heating, cooling, and ventilation. It typically includes fans, filters, heating/cooling coils, humidifiers, and dampers.
AHUs bring in outside or recirculated air, condition it (through heating, cooling, humidifying, or dehumidifying), and distribute it via ductwork. Commonly used in commercial and industrial settings, they help maintain indoor air quality, control temperature, and ensure proper ventilation.
Insulation

Thermal insulation minimizes the transfer of heat between spaces, helping to maintain desired temperatures and reduce energy consumption for heating or cooling.
SGCI understands the importancy of insulation to prevent energy loss and condensation, maintaining efficient operation of HVAC systems. Good insulation helps regulate temperatures and improve energy efficiency.
IoT
IoT solutions connect smart devices and sensors to enhance efficiency across various applications. By collecting real-time data, they enable businesses to monitor systems, optimize operations, and improve decision-making.
With seamless device communication, IoT facilitates automated controls and energy management, leading to increased productivity and reduced costs while creating smarter, more sustainable environments.
Heat Pump
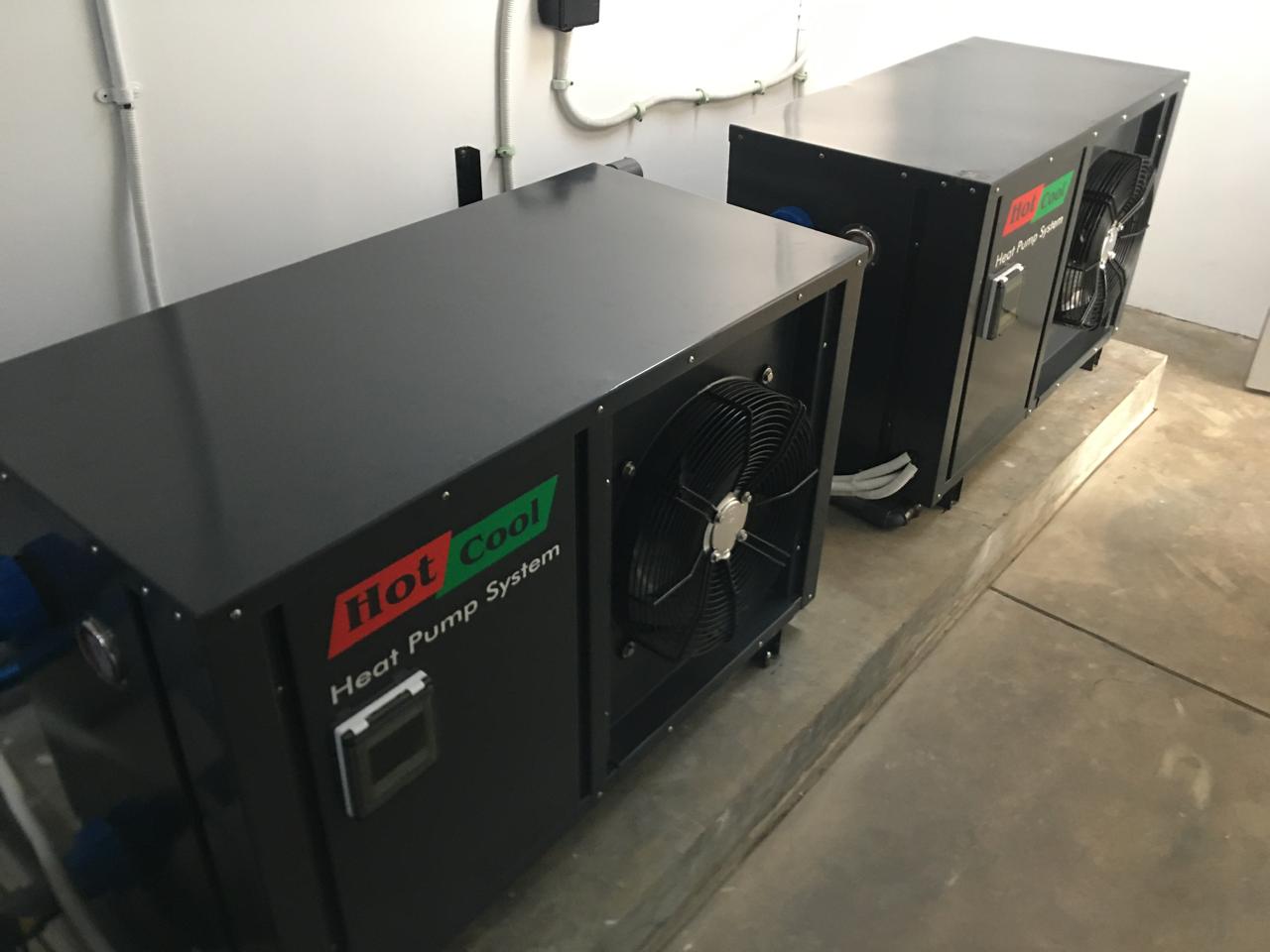

Heat pump is a device that could transfer heat from one location to another using a refrigeration cycle. It can extract heat from a cold space and transfer it to a warmer space, making the warmer space warmer and the colder space cooler.
Heat pumps are more energy-efficient than traditional heating methods. They are often used in conjunction with HVAC systems to provide both heating and cooling.
Ventilation Fan
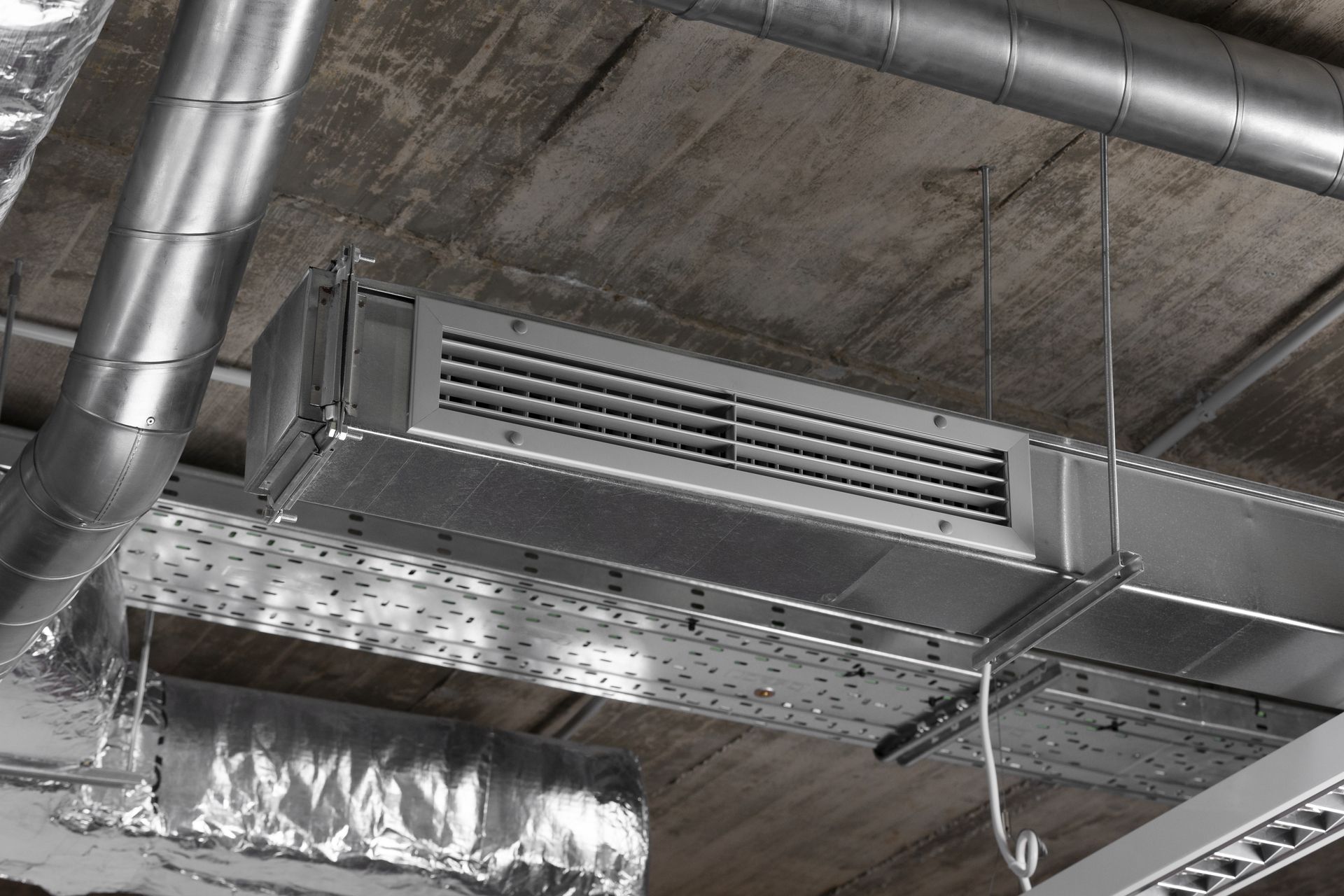

Ventilation systems improve indoor air quality by replacing stale air with fresh air, creating a comfortable environment for occupants. They use fans and ductwork to circulate air, effectively removing contaminants and moisture. Unlike other cooling methods, these systems prioritize air exchange to maintain optimal humidity and reduce pollutants. Available in various configurations, ventilation systems can be tailored to fit any space, providing efficient air distribution while minimizing energy consumption.
Unitary Product
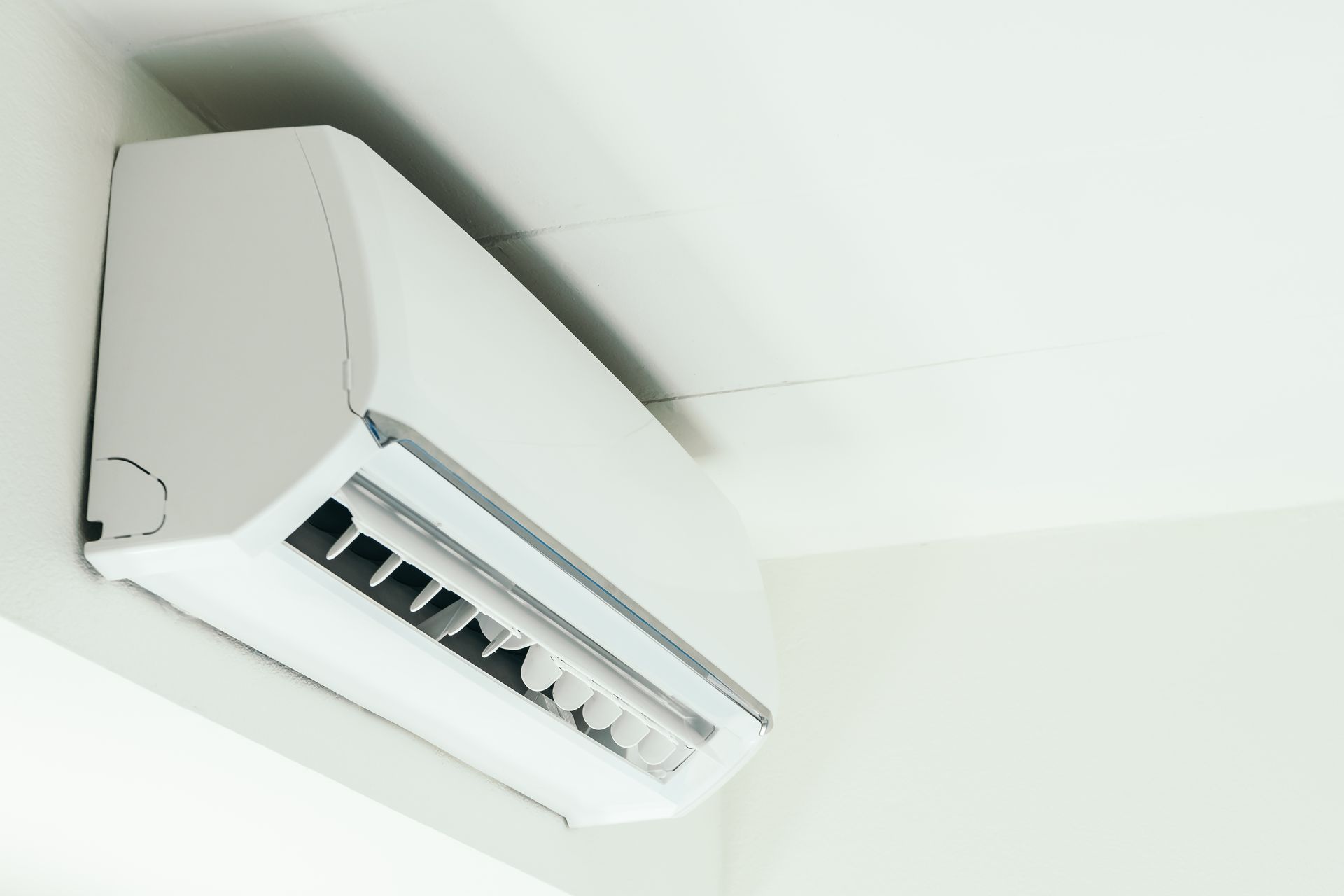

Unitary products are compact HVAC systems that efficiently heat and cool residential and commercial spaces. Combining compressors, evaporators, and condensers in one unit, they simplify installation and maintenance.
Designed for reliable performance and energy efficiency, these systems optimize indoor climate control while minimizing energy use, making them ideal for various space requirements.
VRF

Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems are advanced climate control solutions designed for efficient heating and cooling in commercial and residential spaces. By connecting multiple indoor units to a single outdoor unit, VRF technology optimizes energy use, adjusting refrigerant flow based on real-time demand.
This enables precise temperature control while minimizing energy consumption. With quiet operation and seamless integration into existing structures, VRF systems offer a sustainable choice for comfortable indoor environments.
Green Building Certification

The Green Building Certificate recognizes structures that meet rigorous standards for sustainability and energy efficiency. This certification process evaluates various aspects of a building, including resource use, energy performance, and indoor environmental quality. By achieving this certification, buildings demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impact, promoting occupant health, and enhancing overall sustainability.
Chiller

is a type of cooling system that removes heat from a building or industrial process by transferring it to the surrounding air. It uses fans to blow air over the condenser coils, where the refrigerant releases heat and cools down. Unlike water-cooled chillers, air-cooled chillers do not require cooling towers or water, making them easier to install and maintain.
Ducting

SGCI offers proper design and installation of ducting, essential for efficient airflow, energy conservation, and indoor air quality. In HVAC systems, ducting distributes heated or cooled air, including SUPPLY AIR DUCTS that deliver conditioned air to rooms and RETURN AIR DUCTS that return air to the unit for reconditioning.
EXHAUST AIR DUCT is used to exhaust air or gases from kitchens, bathrooms, laboratories, industrial processes, and other spaces where ventilation is necessary to remove pollutants, odors, or excess heat.
Chilled Water Piping

Chilled water piping and accessories are components used in a chilled water system to circulate cold water between the chiller and air handling units (AHUs) or fan coil units (FCUs) for cooling purposes. The chilled water absorbs heat from the building's air and is then pumped back to the chiller to be cooled again.
Pump

Pump systems efficiently move fluids across various applications, including industrial processes, HVAC systems, and water management. Utilizing mechanical energy, these systems ensure consistent flow and pressure while handling a wide range of liquids. Available in types like centrifugal and positive displacement, pumps can be tailored to meet specific operational needs, enhancing productivity and sustainability in diverse industries.
Cooling Tower

A cooling tower is a heat rejection device used to remove excess heat from a building or industrial process by cooling water. It works by transferring heat from the water to the outside air through evaporation.
Warm water from the system is pumped to the cooling tower, where it is sprayed over fill material to increase surface area. As air flows through the tower, some of the water evaporates, taking heat away with it and cooling the remaining water, which is then recirculated.
Air Handling Unit

An AHU is a device in HVAC systems that regulates and circulates air for heating, cooling, and ventilation. It typically includes fans, filters, heating/cooling coils, humidifiers, and dampers.
AHUs bring in outside or recirculated air, condition it (through heating, cooling, humidifying, or dehumidifying), and distribute it via ductwork. Commonly used in commercial and industrial settings, they help maintain indoor air quality, control temperature, and ensure proper ventilation.
Insulation

Thermal insulation minimizes the transfer of heat between spaces, helping to maintain desired temperatures and reduce energy consumption for heating or cooling.
SGCI understands the importancy of insulation to prevent energy loss and condensation, maintaining efficient operation of HVAC systems. Good insulation helps regulate temperatures and improve energy efficiency.
IoT

IoT solutions connect smart devices and sensors to enhance efficiency across various applications. By collecting real-time data, they enable businesses to monitor systems, optimize operations, and improve decision-making.
With seamless device communication, IoT facilitates automated controls and energy management, leading to increased productivity and reduced costs while creating smarter, more sustainable environments.
Heat Pump

Heat pump is a device that could transfer heat from one location to another using a refrigeration cycle. It can extract heat from a cold space and transfer it to a warmer space, making the warmer space warmer and the colder space cooler.
Heat pumps are more energy-efficient than traditional heating methods. They are often used in conjunction with HVAC systems to provide both heating and cooling.
Ventilation Fan

Ventilation systems improve indoor air quality by replacing stale air with fresh air, creating a comfortable environment for occupants. They use fans and ductwork to circulate air, effectively removing contaminants and moisture. Unlike other cooling methods, these systems prioritize air exchange to maintain optimal humidity and reduce pollutants. Available in various configurations, ventilation systems can be tailored to fit any space, providing efficient air distribution while minimizing energy consumption.
Unitary Product

Unitary products are compact HVAC systems that efficiently heat and cool residential and commercial spaces. Combining compressors, evaporators, and condensers in one unit, they simplify installation and maintenance.
Designed for reliable performance and energy efficiency, these systems optimize indoor climate control while minimizing energy use, making them ideal for various space requirements.
VRF

Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems are advanced climate control solutions designed for efficient heating and cooling in commercial and residential spaces. By connecting multiple indoor units to a single outdoor unit, VRF technology optimizes energy use, adjusting refrigerant flow based on real-time demand.
This enables precise temperature control while minimizing energy consumption. With quiet operation and seamless integration into existing structures, VRF systems offer a sustainable choice for comfortable indoor environments.
Green Building Certification

The Green Building Certificate recognizes structures that meet rigorous standards for sustainability and energy efficiency. This certification process evaluates various aspects of a building, including resource use, energy performance, and indoor environmental quality. By achieving this certification, buildings demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impact, promoting occupant health, and enhancing overall sustainability.

Cooling Tower
A cooling tower is a heat rejection device used to remove excess heat from a building or industrial process by cooling water. It works by transferring heat from the water to the outside air through evaporation.
Warm water from the system is pumped to the cooling tower, where it is sprayed over fill material to increase surface area. As air flows through the tower, some of the water evaporates, taking heat away with it and cooling the remaining water, which is then recirculated.
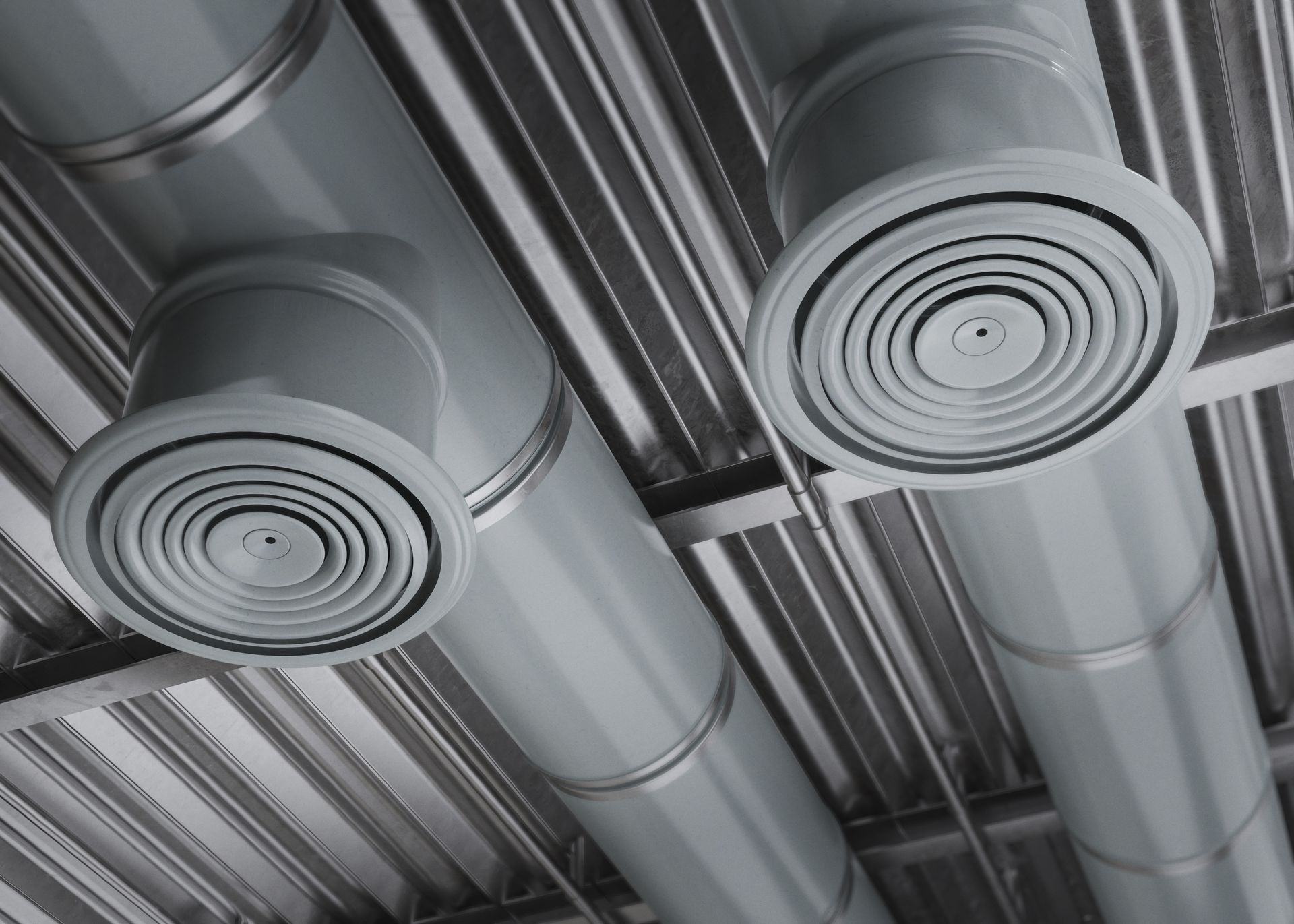

Ducting
SGCI offers proper design and installation of ducting, essential for efficient airflow, energy conservation, and indoor air quality. In HVAC systems, ducting distributes heated or cooled air, including SUPPLY AIR DUCTS that deliver conditioned air to rooms and RETURN AIR DUCTS that return air to the unit for reconditioning.
EXHAUST AIR DUCT is used to exhaust air or gases from kitchens, bathrooms, laboratories, industrial processes, and other spaces where ventilation is necessary to remove pollutants, odors, or excess heat.

Insulation
Thermal insulation minimizes the transfer of heat between spaces, helping to maintain desired temperatures and reduce energy consumption for heating or cooling.
SGCI understands the importancy of insulation to prevent energy loss and condensation, maintaining efficient operation of HVAC systems. Good insulation helps regulate temperatures and improve energy efficiency.
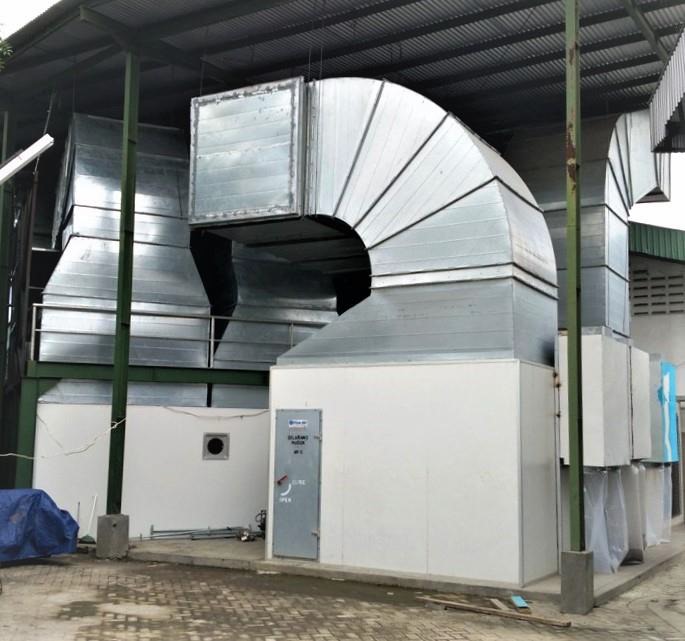

Ventilation Fan
Ventilation systems improve indoor air quality by replacing stale air with fresh air, creating a comfortable environment for occupants. They use fans and ductwork to circulate air, effectively removing contaminants and moisture. Unlike other cooling methods, these systems prioritize air exchange to maintain optimal humidity and reduce pollutants. Available in various configurations, ventilation systems can be tailored to fit any space, providing efficient air distribution while minimizing energy consumption.

Heat Pump
Heat pump is a device that could transfer heat from one location to another using a refrigeration cycle. It can extract heat from a cold space and transfer it to a warmer space, making the warmer space warmer and the colder space cooler.
Heat pumps are more energy-efficient than traditional heating methods. They are often used in conjunction with HVAC systems to provide both heating and cooling.

Pump
Pump systems efficiently move fluids across various applications, including industrial processes, HVAC systems, and water management. Utilizing mechanical energy, these systems ensure consistent flow and pressure while handling a wide range of liquids. Available in types like centrifugal and positive displacement, pumps can be tailored to meet specific operational needs, enhancing productivity and sustainability in diverse industries.

Air Handling Unit
An AHU is a device in HVAC systems that regulates and circulates air for heating, cooling, and ventilation. It typically includes fans, filters, heating/cooling coils, humidifiers, and dampers.
AHUs bring in outside or recirculated air, condition it (through heating, cooling, humidifying, or dehumidifying), and distribute it via ductwork. Commonly used in commercial and industrial settings, they help maintain indoor air quality, control temperature, and ensure proper ventilation.
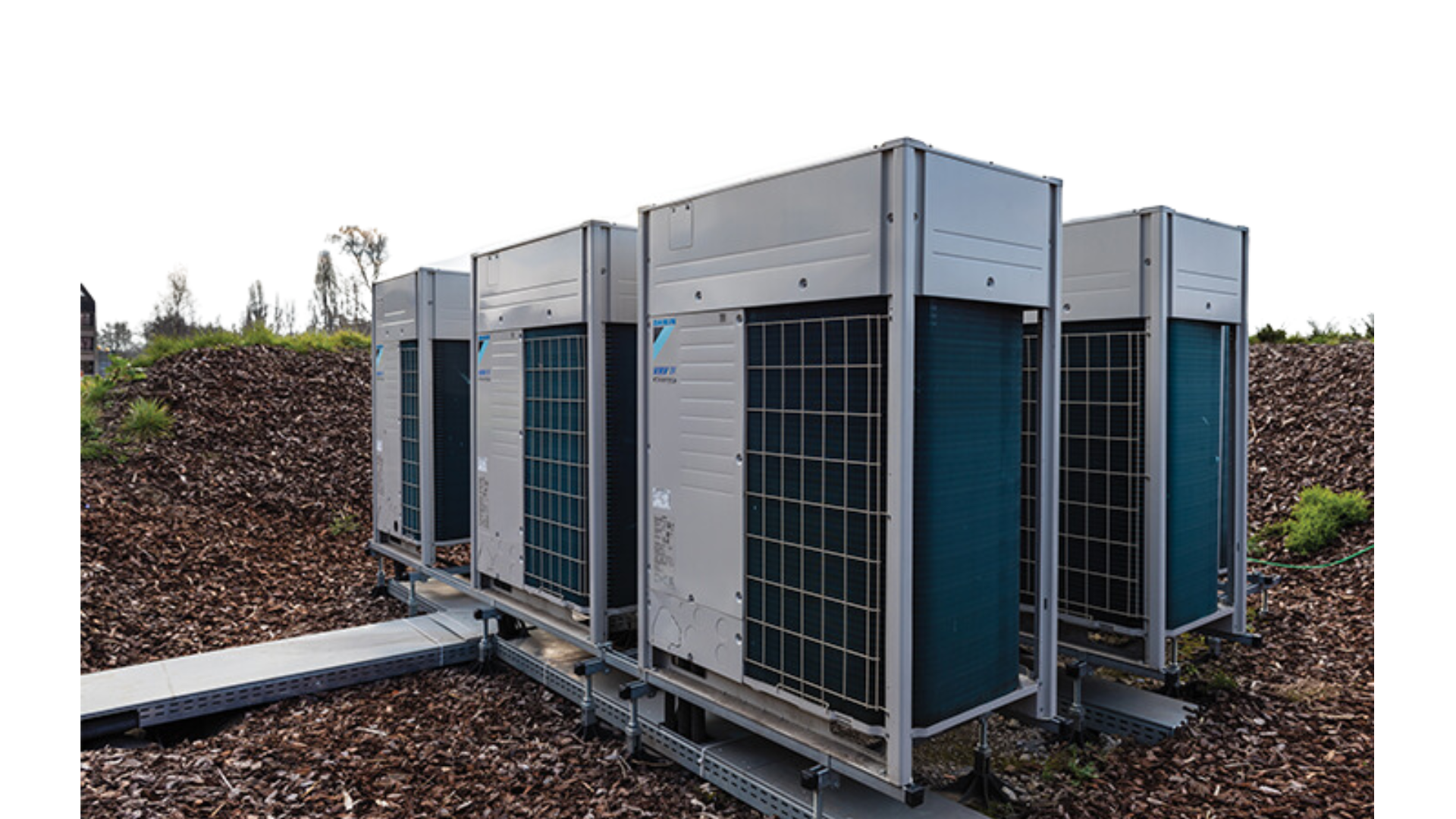

Variable Refrigerant Flow
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems are advanced climate control solutions designed for efficient heating and cooling in commercial and residential spaces. By connecting multiple indoor units to a single outdoor unit, VRF technology optimizes energy use, adjusting refrigerant flow based on real-time demand.
This enables precise temperature control while minimizing energy consumption. With quiet operation and seamless integration into existing structures, VRF systems offer a sustainable choice for comfortable indoor environments.

Internet of Things
IoT solutions connect smart devices and sensors to enhance efficiency across various applications. By collecting real-time data, they enable businesses to monitor systems, optimize operations, and improve decision-making.
With seamless device communication, IoT facilitates automated controls and energy management, leading to increased productivity and reduced costs while creating smarter, more sustainable environments.

Green Building Certificate
The Green Building Certificate recognizes structures that meet rigorous standards for sustainability and energy efficiency. This certification process evaluates various aspects of a building, including resource use, energy performance, and indoor environmental quality. By achieving this certification, buildings demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impact, promoting occupant health, and enhancing overall sustainability.

Chiller
is a type of cooling system that removes heat from a building or industrial process by transferring it to the surrounding air. It uses fans to blow air over the condenser coils, where the refrigerant releases heat and cools down. Unlike water-cooled chillers, air-cooled chillers do not require cooling towers or water, making them easier to install and maintain.

Unitary Product Content
Unitary products are compact HVAC systems that efficiently heat and cool residential and commercial spaces. Combining compressors, evaporators, and condensers in one unit, they simplify installation and maintenance.
Designed for reliable performance and energy efficiency, these systems optimize indoor climate control while minimizing energy use, making them ideal for various space requirements.

Chilled Water Piping
Chilled water piping and accessories are components used in a chilled water system to circulate cold water between the chiller and air handling units (AHUs) or fan coil units (FCUs) for cooling purposes. The chilled water absorbs heat from the building's air and is then pumped back to the chiller to be cooled again.

Cooling Tower
A cooling tower is a heat rejection device used to remove excess heat from a building or industrial process by cooling water. It works by transferring heat from the water to the outside air through evaporation.
Warm water from the system is pumped to the cooling tower, where it is sprayed over fill material to increase surface area. As air flows through the tower, some of the water evaporates, taking heat away with it and cooling the remaining water, which is then recirculated.

Ducting
SGCI offers proper design and installation of ducting, essential for efficient airflow, energy conservation, and indoor air quality. In HVAC systems, ducting distributes heated or cooled air, including SUPPLY AIR DUCTS that deliver conditioned air to rooms and RETURN AIR DUCTS that return air to the unit for reconditioning.
EXHAUST AIR DUCT is used to exhaust air or gases from kitchens, bathrooms, laboratories, industrial processes, and other spaces where ventilation is necessary to remove pollutants, odors, or excess heat.

Insulation
Thermal insulation minimizes the transfer of heat between spaces, helping to maintain desired temperatures and reduce energy consumption for heating or cooling.
SGCI understands the importancy of insulation to prevent energy loss and condensation, maintaining efficient operation of HVAC systems. Good insulation helps regulate temperatures and improve energy efficiency.

Ventilation Fan
Ventilation systems improve indoor air quality by replacing stale air with fresh air, creating a comfortable environment for occupants. They use fans and ductwork to circulate air, effectively removing contaminants and moisture. Unlike other cooling methods, these systems prioritize air exchange to maintain optimal humidity and reduce pollutants. Available in various configurations, ventilation systems can be tailored to fit any space, providing efficient air distribution while minimizing energy consumption.

Heat Pump
Heat pump is a device that could transfer heat from one location to another using a refrigeration cycle. It can extract heat from a cold space and transfer it to a warmer space, making the warmer space warmer and the colder space cooler.
Heat pumps are more energy-efficient than traditional heating methods. They are often used in conjunction with HVAC systems to provide both heating and cooling.

Pump
Pump systems efficiently move fluids across various applications, including industrial processes, HVAC systems, and water management. Utilizing mechanical energy, these systems ensure consistent flow and pressure while handling a wide range of liquids. Available in types like centrifugal and positive displacement, pumps can be tailored to meet specific operational needs, enhancing productivity and sustainability in diverse industries.

Air Handling Unit
An AHU is a device in HVAC systems that regulates and circulates air for heating, cooling, and ventilation. It typically includes fans, filters, heating/cooling coils, humidifiers, and dampers.
AHUs bring in outside or recirculated air, condition it (through heating, cooling, humidifying, or dehumidifying), and distribute it via ductwork. Commonly used in commercial and industrial settings, they help maintain indoor air quality, control temperature, and ensure proper ventilation.

Variable Refrigerant Flow
Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems are advanced climate control solutions designed for efficient heating and cooling in commercial and residential spaces. By connecting multiple indoor units to a single outdoor unit, VRF technology optimizes energy use, adjusting refrigerant flow based on real-time demand.
This enables precise temperature control while minimizing energy consumption. With quiet operation and seamless integration into existing structures, VRF systems offer a sustainable choice for comfortable indoor environments.

Internet of Things
IoT solutions connect smart devices and sensors to enhance efficiency across various applications. By collecting real-time data, they enable businesses to monitor systems, optimize operations, and improve decision-making.
With seamless device communication, IoT facilitates automated controls and energy management, leading to increased productivity and reduced costs while creating smarter, more sustainable environments.

Green Building Certificate
The Green Building Certificate recognizes structures that meet rigorous standards for sustainability and energy efficiency. This certification process evaluates various aspects of a building, including resource use, energy performance, and indoor environmental quality. By achieving this certification, buildings demonstrate a commitment to reducing environmental impact, promoting occupant health, and enhancing overall sustainability.

Chiller
is a type of cooling system that removes heat from a building or industrial process by transferring it to the surrounding air. It uses fans to blow air over the condenser coils, where the refrigerant releases heat and cools down. Unlike water-cooled chillers, air-cooled chillers do not require cooling towers or water, making them easier to install and maintain.

Unitary Product Content
Unitary products are compact HVAC systems that efficiently heat and cool residential and commercial spaces. Combining compressors, evaporators, and condensers in one unit, they simplify installation and maintenance.
Designed for reliable performance and energy efficiency, these systems optimize indoor climate control while minimizing energy use, making them ideal for various space requirements.

Chilled Water Piping
Chilled water piping and accessories are components used in a chilled water system to circulate cold water between the chiller and air handling units (AHUs) or fan coil units (FCUs) for cooling purposes. The chilled water absorbs heat from the building's air and is then pumped back to the chiller to be cooled again.
